Preparing the new lifelong learning national strategy? your country Skills Council is taking up new role?
Strategic planning and devising institutional arrangements are system-level activities that refer to the system capacity to translate policies into positive results for the citizens.
Undertaking reviews of institutional settings helps checking their effectiveness, and if changes in the environment call for their update, or if the mechanisms in place support inter-institutional cooperation.
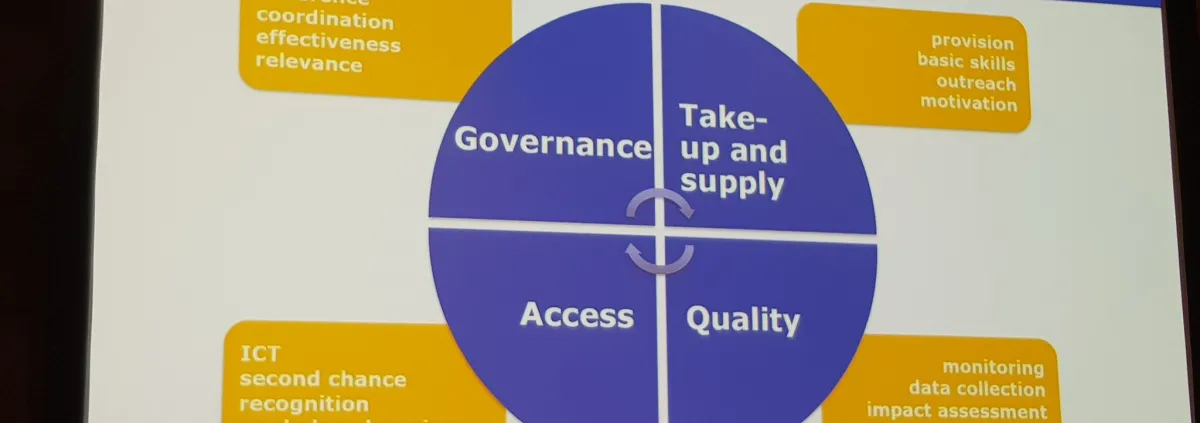
The VET Governance Toolkit helps carrying out this review. The Toolkit builds on the multilevel governance approach, according to which systems function better with inter-institutional, multi-actor and national-sub-national cooperation.
Effective coordination and stakeholders’ involvement in decision-making make the attainment of policy objectives more feasible. Partnerships and responsibility sharing have a horizontal dimension within each level of the system; and a vertical dimension that links systemically the national and sub-national levels.
Not a supply-driven blueprint – good multilevel governance is rather an approach to map and analyse systems and processes, discuss strengths and gaps in VET governance, review the fashion in which institutions interact, challenge their functions and ability to coordinate in the area of skills policies. Methods that best fit multilevel governance approaches include policy learning, knowledge exchange, the exploration of case-studies, and peer-learning. Policy mediation, a consultative process involving actors within a country or territory that mutually interact with a view to implementing agreed policies also plays an important role in strengthening governance.
The VET governance toolbox: concepts, methods and tools
The introduction and review of multilevel modes of governance requires support, advice and learning. The ETF’s VET Governance Toolbox provides that, to spark debates and advance on effective multilevel governance of skills development policies. The tools guide the relevant actors’ participation, aiming at agreements on common actions and share responsibilities.
The toolkit contains the following building blocks. Each block introduces the key ideas and thinking behind the approach.
- Block 1 provides the basic ideas and tools of multilevel governance applied to VET.
- Block 2 provides a method for vision building to define a comprehensive VET reform agenda.
- Block 3 deals with the assessment of institutional arrangements to advance implementation.
- Block 4 covers costing, budgeting, financing and funding, as well as data gathering and analysis.
- Block 5 deals with the role of social partners in linking VET policy to labour market needs
- Block 6 examines inter-play of national and sub-national levels, including decentralisation, and place-based policies related to smart growth strategies
- Block 7 highlights the monitoring and assessment of progress in multi-level governance.
The above sequence starts with the development of a shared vision, roadmap and action plan before drilling down into the practical details of implementation. It is however possible to start in any one of these blocks in the Toolkit, depending on the immediate challenge at hand. The ETF values the blending of theoretical frameworks and experience gained by cooperating with partner countries, and the VET Governance Toolkit is a good example of it.
Hi Asgharfeizi, thank you for your question: the VET governance toolkit will be soon uploaded on the ETF Open Space, stay tuned!
256 Thank you very much. I am looking forward